HYDROLOGY
Hydrology is the science which deals with the occurrence, distribution and movement of water on the earth, including that in the atmosphere and below the surface of earth. Water occurs in the atmosphere in the form of vapor, on the surface as water, snow or ice and below the surface as ground water occupying all the voids within the geologic stratum.
Hydrologic Cycle
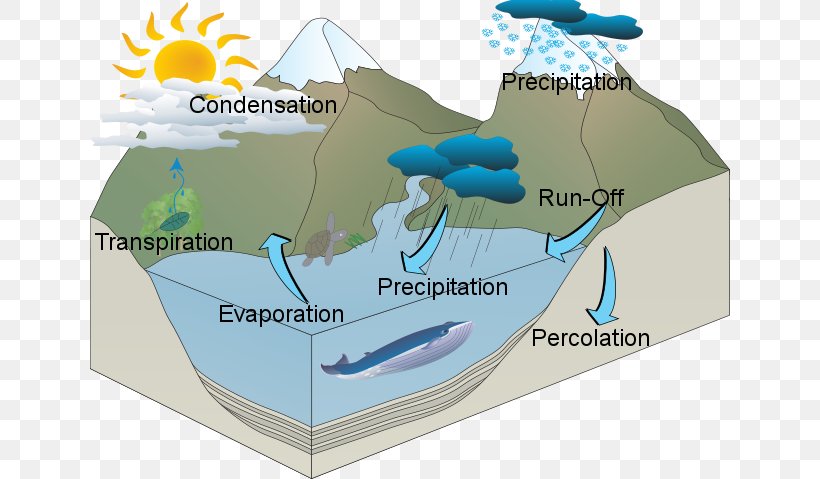
Except for the deep ground water, the total water supply of earth is in constant circulation from earth to atmosphere, and back to earth. The earth’s circulatory system is known as the hydrologic cycle. Hydrologic cycle is the process of transfer of moisture from the atmosphere to the earth in the form of precipitation, conveyance of the precipitated water by streams and rivers to oceans and lakes, and evaporation of water back to the atmosphere.
Precipitation
Precipitation may be defined as the fall of moisture from the atmosphere to the earth surface in any form.
Forms of Precipitation
- Rain
- Snow
- Drizzle
- Glaze
- Sleet
- Hail.
Rain: It consists of water drops mostly
larger than 0.5 mm and smaller than 6 mm in diameter. Drops bigger than 6 mm
tend to break up as they fell.
Type Intensity (mm/hr)
Light Rain < 2.5
Moderate Rain 2.5 to 7.5
Heavy Rain > 7.5
Snow:
It is that type of precipitation
which results from sublimation, i.e., water vapour directly changes into ice.
It falls as white or translucent ice crystals often agglomerated into
snowflakes.
Average density of snow 0.1 g/cm³
The specific gravity of snow is
often taken to be 0.1
Drizzle:
They
are tiny water droplets of size between 0.1 to 0.5 mm which fall with such slow
settling rates that they occasionally appear to float.
As the size and intensity of
Drizzle is very less, they appear to float in air.
Glaze: when
the water droplet ( rain or drizzle ) come in contact with ground which have
the temperature near about 0 °C
or less than it, these water drops freeze and form ice coating on ground
surface which is called glaze or freezing rain.
Sleet: When
the rain drops fall through the layer of sub-freezing air near the earth’s
surface the rain drops get frozen to ice stage. It is called sleet or grains of
ice.
Hail: It
is the precipitation in form of lumps of ice. The hail stones are produced in
convective clouds mostly cumulonimbus. Their shape may be conical, spheroidal
or irregular. The size of hail stones may be anything more than 5 mm.
The
specific gravity of hail stone is about 0.8
Form of Precipitation Fall Speed ( m/sec)
Drizzle Drops 1
Rain Drops 10
Hail 20-50
No comments:
Post a Comment